At What Speed Must I Live in Order to See You Again
I am a erstwhile maths instructor and possessor of DoingMaths. I love writing about maths, its applications and fun mathematical facts.
Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642)

Galileo's Principle of Relativity
Before we look at why time appears to slow down equally y'all travel at speeds approaching the speed of low-cal, we need to go back a few hundred years to look at the work of Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642).
Galileo was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer whose incredible body of work is still highly relevant today and fix the foundations for much of modernistic science.
The attribute of his work we are most interested in here however is his 'Principle of Relativity'. This states that all steady motion is relative and cannot exist detected without reference to an exterior point.
In other words, if you were saturday on a railroad train that was moving along at a smooth, steady rate, you would not be able to tell if you were moving or stationary without looking out of the window and checking if the scenery was moving past.
The Speed of Calorie-free
Another important affair we need to know before we begin is that the speed of low-cal is constant, regardless of the speed of the object emitting this light. In 1887 2 physicists called Albert Michelson (1852 - 1931) and Edward Morley (1838 - 1923) showed this in an experiment. They establish out that it didn't thing if light was travelling with the direction of the Earth'southward rotation or against it, when they measured the speed of lite it was e'er travelling at the same speed.
This speed is 299 792 458 m/south. As this is such a long number, we generally denote it by the letter of the alphabet 'c'.
Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955)

Albert Einstein and His Thought Experiments
At the first of the 20th century, a immature German called Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) was pondering near the speed of light. He imagined that he was sat in a spaceship travelling at the speed of light while looking in a mirror in front of him.
When you look in a mirror, the light that has bounced off you is reflected back towards you by the surface of the mirror, hence you see your own reflection.
Einstein realised that if the spaceship was travelling at the speed of light as well, we now have a trouble. How could the light from y'all always reach the mirror? Both the mirror and the light from yous are travelling at the speed of light, which should mean that the low-cal tin't catch upwardly to the mirror, hence you don't run across a reflection.
But if you lot can't see you reflection, this would warning you to the fact that you are moving at lite speed hence breaking Galileo's principle of relativity. We also know that the low-cal axle can't speed up in order to grab the mirror every bit the speed of light is constant.
Something has to give, but what?
Time
Speed is equal to altitude travelled divided by time taken. Einstein realised that if the speed was not changing, then it must be distance and fourth dimension that are changing.
He created a thought experiment (a purely made-up scenario in his head) to examination out his ideas.
Scroll to Go on
Read More From Owlcation
A Light Clock
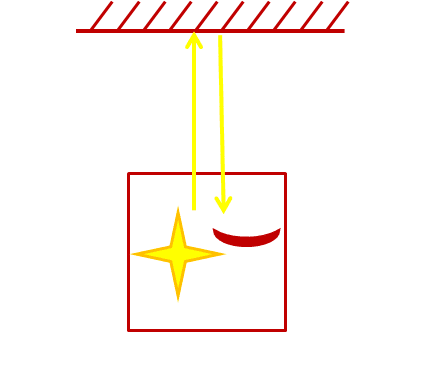
Einstein'south Thought Experiment
Imagine a light clock that looks a piffling similar the pic above. It works by emitting pulses of low-cal at equal time intervals. These pulses travel forward and hit a mirror. They are then reflected back towards a sensor. Each time a light pulse hits the sensor you lot hear a click.
A Moving Calorie-free Clock
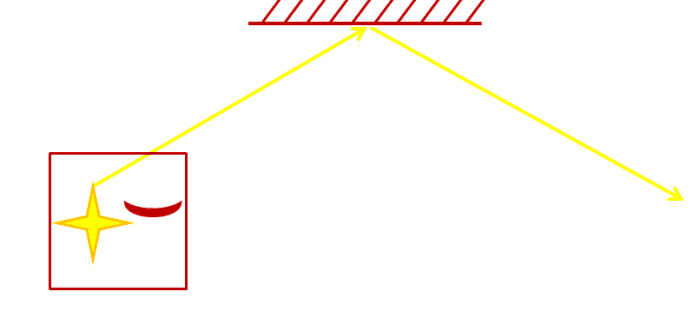
Now suppose this low-cal clock was in a rocket travelling at speed 5 k/s and positioned so that the pulses of light were sent out perpendicularly to the direction of travel of the rocket. Furthermore in that location is a stationary observer watching the rocket travel past. For our experiment suppose the rocket is travelling from the observer's left to right
The light clock emits a pulse of low-cal. By the time the pulse of light has reached the mirror, the rocket has moved frontwards. This means that for the observer stood exterior the rocket looking in, the light beam will be hitting the mirror further right than the point it was emitted from. The pulse of light now reflects dorsum, only once more the whole rocket is moving then the observer sees the light return to the clock sensor at a point further right of the mirror.
The observer would witness the calorie-free travelling in a path similar in the picture above.
A Moving Clock Runs Slower Than a Stationary One, But past How Much?
To summate how much time is changing we will need to do some calculations. Allow
v = the speed of the rocket
t' = the time between clicks for a person in the rocket
t = the time between clicks for the observer
c = the speed of light
L = the distance between the lite pulse emitter and the mirror
Time = distance/speed so on the rocket t'=2L/c (the light travelling to the mirror and back)
All the same for the stationary observer we have seen that the light appears to take a longer path.
The Moving Low-cal Clock
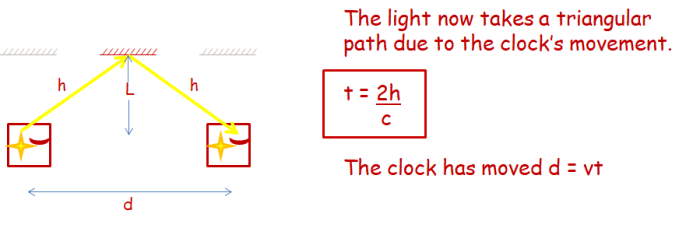
We at present accept a formula for the fourth dimension taken on the rocket and the time taken exterior of the rocket, so let's look at how we tin can bring these together.
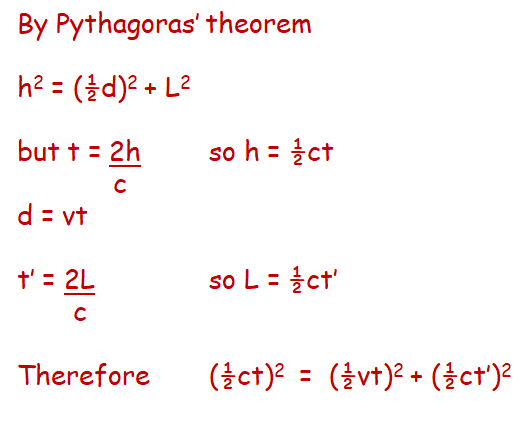
How Time Changes with Speed
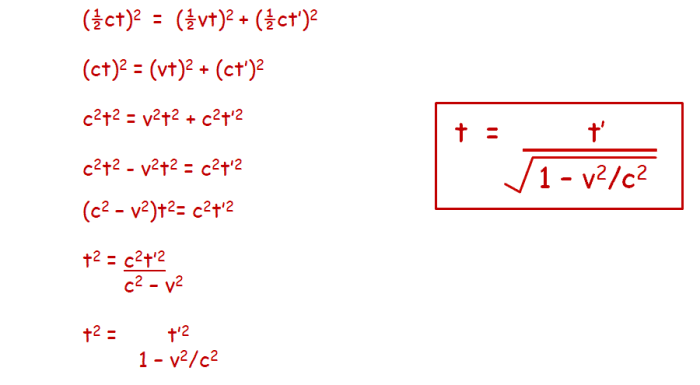
Nosotros have ended upward with the equation:
t= t'/√(1-v2/c2)
This converts between how much time has passed for the person on the rocket (t') and how much fourth dimension has passed for the observer exterior of the rocket (t). You tin see that every bit we are always dividing by a number less than one, and then t is always going to exist bigger than t', hence less time is passing for the person inside the rocket.
Why Does Time Tedious Down - Video from the DoingMaths YouTube Channel
© 2020 David
sellersawrossing1953.blogspot.com
Source: https://owlcation.com/stem/Why-Does-Time-Slow-Down-As-You-Approach-the-Speed-of-Light
0 Response to "At What Speed Must I Live in Order to See You Again"
Post a Comment